FAQs
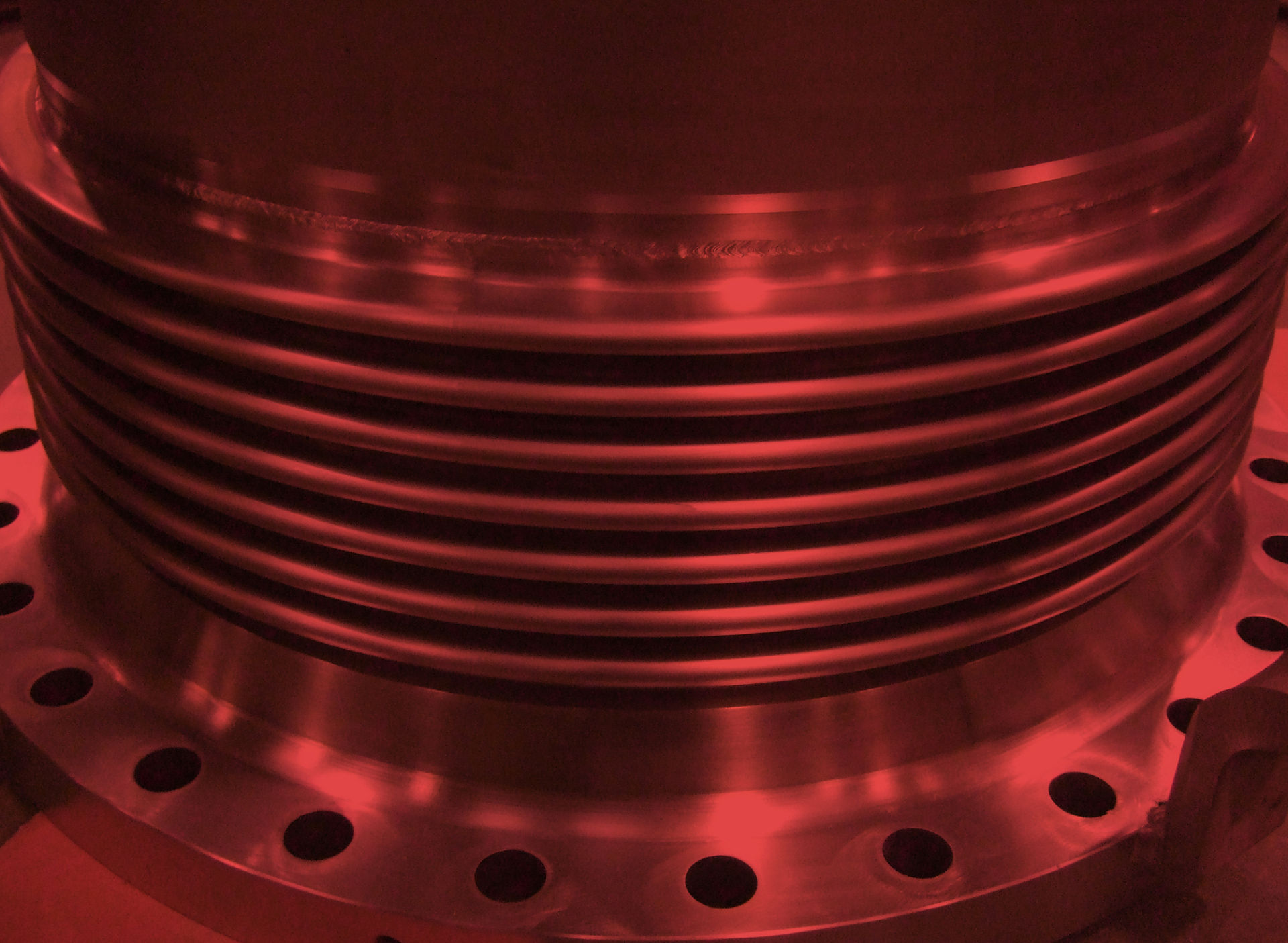
WHAT ARE BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Bellows and expansion joints are flexible components used in piping systems to absorb movement, vibration and thermal expansion. Bellows are typically made of metal and consist of a series of convolutions that allow for flexibility. Expansion joints, which include bellows as a key component, can be metallic, rubber or fabric and are designed to accommodate various types of movement, including axial, lateral and angular displacement, ensuring the integrity and longevity of piping systems.
HOW DO EXPANSION JOINTS WORK? Expansion joints work by allowing controlled movement within a piping system and potentially restricting or limiting other types of movement. They absorb thermal expansion and contraction, reduce vibration and compensate for misalignment. The flexible element, often a metal bellows or rubber/fabric section, expands and contracts as needed, either axially, laterally, angularly or a combination of these, thus protecting the system from stress and potential damage. By accommodating these movements, expansion joints help maintain system integrity and prevent leaks or failures.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Bellows are the flexible, corrugated parts of an expansion joint that allow for movement and flexibility. Expansion joints, on the other hand, are complete assemblies that include bellows and additional components like tie bars, limiting rods and restraints, hinges and gimbal arrangements. While bellows provide the flexibility, expansion joints provide a comprehensive solution to manage movement, pressure and thermal changes within piping systems.
WHAT MATERIALS ARE BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS MADE FROM? Bellows and expansion joints are made from various materials depending on the application. Metallic bellows are typically made from stainless steel or other high-strength alloys for their durability and resistance to high temperatures and pressures. Rubber expansion joints are made from elastomers like EPDM, neoprene or nitrile, which offer good flexibility and chemical resistance. Fabric expansion joints use various materials including fiberglass and silicone-coated fabrics to handle a wide range of temperatures and corrosive environments.
WHERE ARE EXPANSION JOINTS TYPICALLY USED OR REQUIRED? Expansion joints are used in a variety of industries, including power generation, petrochemical, HVAC, water treatment and industrial processing. They are commonly found in piping systems, ductwork and equipment that experience thermal expansion, vibration or misalignment. Specific applications include steam lines, exhaust systems and pump connections, where they help to manage thermal growth, reduce noise and vibration and protect the integrity of the system.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF BELLOWS USED IN INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS? There are several types of bellows used in industrial applications, including single-ply and multi-ply bellows, formed and welded bellows and convoluted and non-convoluted bellows. Single-ply bellows are made from a single layer of material, while multi-ply bellows have multiple layers for added strength. Formed bellows are made by shaping metal sheets and welded bellows are made by welding individual rings or tubes. Convoluted bellows have ridges for flexibility and non-convoluted bellows are smooth for specific applications.
HOW DO I CHOOSE THE RIGHT EXPANSION JOINTS FOR MY APPLICATIONS? Choosing the right expansion joint involves considering several factors, including the type of movement (axial, lateral, angular), pressure and temperature conditions, the material compatibility with the media being transported and the physical space available for installation. It is essential to consult with manufacturers or experts to ensure the expansion joint meets the specific requirements of the application, such as accommodating thermal expansion, reducing vibration and handling the required pressure and temperature ranges. Teddington is a leading specialist in bellows expansion joints and we will always provide assistance in correct selection.
HOW LONG DO EXPANSION JOINTS LAST? The lifespan of an expansion joint depends on several factors, including the material, operating conditions and maintenance practices. Metallic expansion joints can last for many years, depending on the environment and usage, while rubber and fabric expansion joints generally have shorter lifespans, due to the natural degrading of the material. Regular inspections and maintenance can extend the lifespan by identifying and addressing issues before they lead to failure. As a leading member and contributor to the EJMA Standards, Teddington specialises in optimising the lifetime of bellows expansion joints.
HOW DO I INSTALL EXPANSION JOINTS? Proper installation of expansion joints involves several steps. First, ensure the expansion joint is the correct size and type for the application. Align the piping system correctly to avoid misalignment stresses. Install the joint with the specified anchors and guides, ensuring it is not subjected to torsion or excessive displacement during installation. Follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines, including tightening bolts to the recommended torque and checking for leaks after installation. Proper installation ensures optimal performance and longevity of the expansion joint. Teddington will always provide guidance and can even provide in-person assistance in the correct installation and maintenance of bellows expansion joints and associated pipework.
WHAT ARE THE COMMON FAILURE MODES OF BELLOWS? Common failure modes of bellows include fatigue cracking, corrosion, erosion and mechanical damage. Fatigue cracking occurs due to repeated flexing and stress cycles, leading to material failure. Corrosion can result from exposure to aggressive chemicals or environments, weakening the material. Erosion occurs when abrasive particles in the media wear away the bellows surface. Mechanical damage can occur during installation or operation, such as dents, tears or punctures, compromising the bellows' integrity and performance.
WHAT MAINTENANCE IS REQUIRED FOR EXPANSION JOINTS? Maintenance for expansion joints includes regular inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Visual inspections can identify issues like cracks, leaks, or misalignment. Periodic pressure testing can ensure the joint maintains its integrity under operating conditions. Cleaning the joint and surrounding areas can prevent debris buildup that may cause damage. Replacing worn or damaged components and ensuring proper alignment and support are crucial for maintaining the expansion joint's performance and extending its lifespan.
HOW DO EXPANSION JOINTS ACCOMMODATE THERMAL EXPANSION? Expansion joints accommodate thermal expansion by flexing and compressing in response to temperature changes. As the piping system heats up, the material expands and the bellows within the expansion joint compress to absorb the movement. Conversely, when the system cools down, the bellows extend to accommodate the contraction. This flexibility prevents stress on the piping system, reduces the risk of leaks or fractures and maintains the system's structural integrity.
WHAT IS THE MAXIMUM TEMPERATURE FOR BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? The maximum temperature for bellows and expansion joints depends on the material. Metallic bellows, made from stainless steel or high-temperature alloys, can withstand temperatures up to 1000°F (538°C) or higher. Rubber expansion joints, using materials like EPDM or silicone, typically handle temperatures up to 300°F (149°C). Fabric expansion joints, with materials such as PTFE or fiberglass, can endure temperatures ranging from 500°F (260°C) to over 2000°F (1093°C), depending on the specific construction and application.
CAN EXPANSION JOINTS BE USED IN HIGH-PRESSURE APPLICATIONS? Yes, expansion joints can be used in high-pressure applications, but they must be designed and constructed to handle the specific pressure requirements. Metallic expansion joints are often used in high-pressure environments due to their strength and durability. These joints are designed with thicker materials, reinforced layers and pressure-balanced configurations to withstand the high pressure. It is essential to select an expansion joint rated for the specific pressure and follow the manufacturer's guidelines to ensure safe and reliable operation.
WHAT INDUSTRIES USE BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Bellows and expansion joints are used across various industries, including power generation, petrochemical, oil and gas, HVAC, water treatment and industrial processing. In power generation, they accommodate thermal expansion in steam lines and exhaust systems. The petrochemical and oil and gas industries use them in pipelines and processing equipment to manage thermal growth and vibration. HVAC systems use expansion joints to reduce noise and vibration. Water treatment plants use them in piping systems to handle movement and prevent leaks. Industrial processing plants use them in equipment and piping systems to ensure reliability and longevity.
HOW DO YOU MEASURE FOR A REPLACEMENT EXPANSION JOINT? To measure for a replacement expansion joint, start by identifying the type and size of the existing joint. Measure the face-to-face length, flange or end connection dimensions and the overall diameter. Note the type of movement (axial, lateral, or angular) the joint needs to accommodate and the maximum range of motion required. Record the operating pressure and temperature, as well as the material of the existing joint. Providing these measurements to the manufacturer or supplier will help ensure you get a compatible replacement that meets your system's specifications.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF USING METALLIC BELLOWS? Metallic bellows offer several benefits, including high strength and durability, resistance to high temperatures and pressures and excellent corrosion resistance when made from appropriate alloys. They can accommodate various types of movement, including axial, lateral and angular displacement and provide reliable performance in demanding environments. Metallic bellows are also relatively compact, making them suitable for applications with limited space. Their robust construction ensures a long service life and reduces the need for frequent replacements, making them cost-effective over time.
HOW DO RUBBER EXPANSION JOINTS DIFFER FROM METAL EXPANSION JOINTS? Rubber expansion joints differ from metal expansion joints in material composition and application suitability. Rubber joints, made from elastomers like EPDM, neoprene, or nitrile, offer excellent flexibility, vibration dampening and chemical resistance. They are ideal for applications with lower pressure and temperature requirements, such as HVAC systems and water treatment plants. Metal expansion joints, made from stainless steel or other alloys, are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. They provide greater strength and durability but may require more precise alignment and support during installation.
WHAT IS AXIAL MOVEMENT IN THE CONTEXT OF EXPANSION JOINTS? Axial movement refers to the compression and extension along the axis of the expansion joint. This type of movement occurs when the piping system expands or contracts due to temperature changes or pressure fluctuations. Axial movement is accommodated by the flexible element within the expansion joint, such as the bellows, which compresses or extends to absorb the displacement. Properly designed expansion joints can handle significant axial movement, reducing stress on the piping system and preventing damage.
HOW DO EXPANSION JOINTS REDUCE VIBRATION AND NOISE? Expansion joints reduce vibration and noise by absorbing and dampening the energy transmitted through the piping system. The flexible elements, such as rubber or metal bellows, isolate vibrations and prevent them from propagating throughout the system. This reduces the noise generated by vibrating pipes and equipment and minimises the risk of damage due to vibration-induced stress. By effectively managing vibration and noise, expansion joints contribute to a quieter, more stable and longer-lasting piping system.
CAN EXPANSION JOINTS BE CUSTOMISED? Yes, expansion joints can be customised to meet specific application requirements. Customisation options include selecting materials compatible with the fluid and operating conditions, designing the joint to accommodate specific movements (axial, lateral, or angular) and choosing the appropriate end connections (flanges, threaded, or welded). Manufacturers can also tailor the size, pressure rating and temperature tolerance to fit the unique needs of a particular system. Custom expansion joints ensure optimal performance and longevity by addressing the specific challenges and demands of the application.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS THAT AN EXPANSION JOINT NEEDS TO BE REPLACED? Signs that an expansion joint needs to be replaced include visible cracks, leaks or tears in the flexible element, corrosion or rust on metal components and significant deformation or misalignment. Other indicators include unusual noises, such as banging or clanging, increased vibration or reduced performance of the system. Regular inspections can help identify these signs early, allowing for timely replacement and preventing potential system failures or costly repairs.
HOW DO YOU TEST THE INTEGRITY OF AN EXPANSION JOINT? Testing the integrity of an expansion joint involves visual inspections, pressure tests and non-destructive testing methods. Visual inspections check for signs of wear, corrosion and damage. Pressure tests, such as hydrostatic or pneumatic testing, apply pressure to the joint to ensure it can handle the operating conditions without leaking. Non-destructive testing methods, like dye penetrant, ultrasonic, or radiographic inspection, can detect cracks, defects, or material degradation without damaging the joint. Regular testing ensures the expansion joint remains reliable and safe for operation.
WHAT ARE FABRIC EXPANSION JOINTS USED FOR? Fabric expansion joints are used in applications where high flexibility and the ability to handle large movements are required. They are commonly found in ducting systems for air, gas and flue gas handling, such as in power plants, refineries and industrial processing facilities. Fabric expansion joints can accommodate significant thermal expansion, vibration and misalignment while providing excellent chemical resistance and temperature tolerance. They are particularly useful in applications where metal or rubber joints may not be suitable due to space constraints or extreme operating conditions.
WHAT STANDARDS GOVERN THE MANUFACTURING OF BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Several standards govern the manufacturing of bellows and expansion joints, mainly the EJMA (Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association) standards, which provide guidelines for design, materials and testing of metallic expansion joints. There are other standards too, such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) codes, such as the Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) and the B31 series for piping, ISO (International Organisation for Standardisation) and many more.
HOW DO YOU CALCULATE THE REQUIRED EXPANSION JOINT SIZE? Calculating the required expansion joint size involves determining the amount and type of movement the joint needs to accommodate, the pressure and temperature conditions and the dimensions of the piping system. Start by measuring the expected thermal expansion or contraction, lateral displacement and angular rotation. Use these measurements to select an expansion joint that can handle the specified movements. Consider the operating pressure and temperature to choose materials and designs that meet the requirements. Consulting with manufacturers or using design software can help ensure accurate calculations and proper sizing.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A SINGLE AND A DOUBLE BELLOWS EXPANSION JOINT? A single bellows expansion joint consists of one set of bellows and is typically used for axial movement. A double bellows expansion joint, also known as a universal expansion joint, has two sets of bellows connected by a centre pipe or spool. The double bellows design allows for greater flexibility and can accommodate larger lateral and angular movements in addition to axial displacement. The choice between single and double bellows depends on the specific movement requirements and space constraints of the application.
ARE THERE ANY SPECIAL STORAGE REQUIREMENTS FOR BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Yes, there are special storage requirements for bellows and expansion joints to prevent damage and degradation. Store them in a clean, dry and temperature-controlled environment to avoid exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures and corrosive substances. Protect the joints from mechanical damage by keeping them in their original packaging or using protective covers. Ensure that they are not subjected to any loads or stresses during storage. Following these guidelines helps maintain the integrity and performance of the expansion joints until they are ready for installation.
HOW DOES PRESSURE AFFECT THE SELECTION OF AN EXPANSION JOINT? Pressure significantly affects the selection of an expansion joint, as it determines the strength and design requirements. High-pressure applications require expansion joints made from robust materials, such as stainless steel or high-strength alloys and may need reinforced designs, such as multi-ply bellows or pressure-balanced configurations. The joint must be rated to handle the maximum operating pressure and potential pressure surges. Proper selection ensures the joint can withstand the pressure without failing or deforming, maintaining system integrity and safety.
WHAT ROLE DO EXPANSION JOINTS PLAY IN PIPING SYSTEMS? Expansion joints play a crucial role in piping systems by accommodating thermal expansion and contraction, reducing vibration and noise, compensating for misalignment and relieving stress on the pipes and equipment. They help maintain the structural integrity and reliability of the system, preventing leaks, fractures and other failures. By allowing controlled movement and flexibility, expansion joints ensure the smooth operation of piping systems in various industries, including power generation, petrochemical, HVAC and water treatment.
HOW DO YOU PREVENT CORROSION IN BELLOWS AND EXPANSION JOINTS? Preventing corrosion in bellows and expansion joints involves selecting appropriate materials, applying protective coatings and maintaining proper operating conditions. Using corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, Inconel or PTFE-lined bellows, can significantly reduce the risk of corrosion. Protective coatings, such as paint or galvanization, provide an additional barrier against corrosive elements. Regular inspections and maintenance, including cleaning and monitoring for signs of corrosion, help address issues early and extend the lifespan of the joints.
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF AN EXTERNAL COVER ON AN EXPANSION JOINT? The purpose of an external cover on an expansion joint is to protect the bellows from external damage, contamination and environmental exposure. The cover shields the bellows from mechanical impacts, debris and corrosive substances, helping to prevent punctures, abrasion and corrosion. Additionally, external covers can help retain insulation, reduce heat loss and improve the aesthetic appearance of the installation. By providing this protection, the cover helps ensure the reliable performance and longevity of the expansion joint.
HOW DO EXPANSION JOINTS HANDLE LATERAL MOVEMENT? Expansion joints handle lateral movement through the flexibility of the bellows or other flexible elements. The joint's design allows it to bend and flex sideways, accommodating displacement perpendicular to the axis of the piping system. Double bellows or universal expansion joints are particularly effective at handling lateral movement, as they have two sets of bellows connected by a centre pipe, providing greater flexibility. Proper installation with guides and anchors ensures the joint moves as intended without causing undue stress on the system.
WHAT IS A HINGED EXPANSION JOINT? A hinged expansion joint is designed to accommodate angular movement in one plane. It consists of a bellows element connected to hinge plates or pins, allowing the joint to bend at a fixed angle. The hinges restrict axial and lateral movement, ensuring the joint only moves in the specified angular direction. Hinged expansion joints are commonly used in systems with significant angular displacement, such as piping connected to rotating equipment or systems with large directional changes.
WHAT ARE UNIVERSAL EXPANSION JOINTS USED FOR? Universal expansion joints, also known as double bellows expansion joints, are used to accommodate multiple types of movement, including axial, lateral and angular displacement. They consist of two bellows connected by a centre pipe or spool, providing greater flexibility and movement absorption. Universal expansion joints are ideal for applications where the piping system experiences complex movements, such as thermal expansion in multiple directions or combined axial and lateral displacement.
HOW DO EXPANSION JOINTS IN BRIDGES DIFFER FROM THOSE IN PIPELINES? Expansion joints in bridges differ from those in pipelines in terms of design and functionality. Bridge expansion joints are designed to accommodate large movements caused by thermal expansion, traffic loads and structural shifts. They often include features like sliding plates, rubber seals and modular systems to handle significant displacement and ensure smooth transitions for vehicles. Pipeline expansion joints, on the other hand, are designed to manage thermal expansion, vibration and pressure changes within a contained fluid system. They typically use bellows or flexible materials to absorb movement and prevent stress on the piping.
.png)